A Geothermal Gold Rush: Unlocking the Potential of Sustainable Energy

Did you know that geothermal energy could supply up to 20% of the world’s electricity by 2050? This shift is sparking what many are calling “the new gold rush: investing in geothermal energy projects and tech.” Investors are now eyeing this sustainable energy source as a way to diversify their portfolios.
Geothermal energy offers reliable returns and plays a crucial role in combating climate change. With advancements in technology, the potential for profit in the geothermal energy project has never been higher, especially for the energy firm involved in networked geothermal projects. This blog post explores why geothermal projects are becoming essential investments and how they can benefit both your finances and the planet. Get ready to dive into the exciting world of geothermal energy and discover why it’s time to join this booming trend.
Key Takeaways
- Geothermal energy is a promising investment opportunity, as it offers a reliable and renewable energy source with significant growth potential.
- Understand the benefits and risks associated with geothermal investments by researching specific projects and their environmental impacts.
- Look for innovations in geothermal technology that can enhance efficiency and reduce costs, increasing the likelihood of financial returns.
- Consider the long-term sustainability of geothermal projects, as they can provide stable energy solutions while contributing to climate goals.
- Evaluate the financial returns of geothermal investments by analyzing past performance and market trends to make informed decisions.
- Stay updated on the evolving landscape of geothermal energy to identify new opportunities and ensure your investments remain relevant.
Understanding Geothermal Energy Potential
Definition
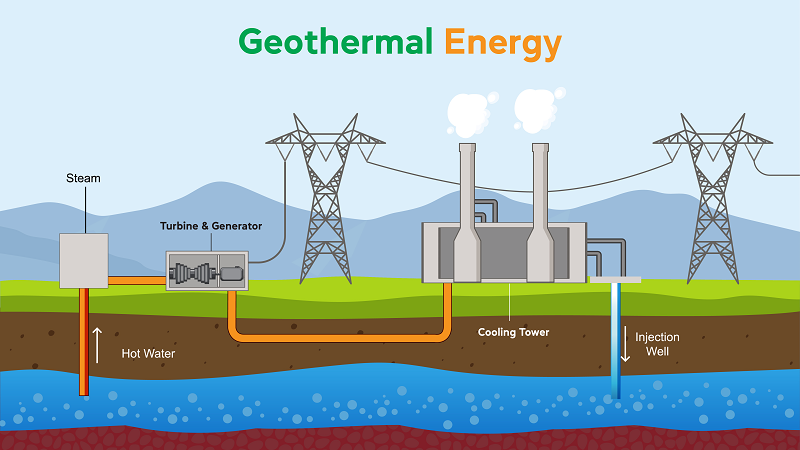
Geothermal energy comes from the heat stored beneath the Earth’s surface. This energy originates from the Earth’s formation and radioactive decay of minerals. It can be harnessed by drilling wells into geothermal reservoirs. These wells bring hot water or steam to the surface for geothermal energy generation. This steam can then be used to generate electricity or provide direct heating.
Mechanism of Harnessing
Geothermal energy works through a simple but effective process. Hot water or steam is extracted from underground reservoirs. The steam drives turbines connected to generators, producing electricity. Alternatively, the hot water can be used directly for heating buildings or in industrial processes.
The technology has improved over the years, making it easier and more efficient to tap into these resources. Enhanced geothermal systems (EGS) allow drilling in areas without natural reservoirs. This expands the potential for geothermal projects significantly.
Sustainability
Geothermal energy is a renewable resource. Unlike fossil fuels, it does not deplete over time. As long as the Earth exists, geothermal energy will remain available. The sustainability of this resource makes it an attractive investment option.
Moreover, geothermal plants have a low environmental impact compared to traditional power sources. They produce minimal greenhouse gas emissions. This aligns with global efforts to combat climate change and transition to cleaner energy sources.
Geographical Locations
Certain regions have higher geothermal potential than others. Countries along the Pacific Ring of Fire are particularly rich in geothermal resources. This includes nations like:
- Iceland: Known for its extensive geothermal activity, Iceland generates about 90% of its heating from geothermal sources.
- United States: The U.S. has significant geothermal power plants, especially in California and Nevada.
- Philippines: It ranks second in the world for geothermal electricity production.
Other countries with promising geothermal sites include New Zealand, Italy, and Indonesia. Each location offers unique opportunities for investment in geothermal projects.
Investors should consider these geographical advantages when exploring options in geothermal energy. The potential for growth in this sector is substantial, given the increasing demand for clean energy solutions.
The Rise of Geothermal Energy Sector
Global Interest
Growing interest in geothermal energy has surged in recent years. Many countries are investing heavily in geothermal projects. This shift is due to the urgent need for renewable energy sources. Geothermal energy production offers a reliable alternative to fossil fuels.
The global market for geothermal power generation is projected to reach $60 billion by 2026. Countries like the United States, Indonesia, and the Philippines lead in geothermal electricity generation. These nations have rich hydrothermal resources that can be tapped for energy.
Key Players
Several companies dominate the geothermal energy sector. Leading firms include Ormat Technologies, Calpine Corporation, and Enel Green Power. These companies invest in geothermal field development and operate multiple plants worldwide.
Ormat Technologies focuses on developing geothermal power plants and energy storage solutions. Calpine Corporation operates one of the largest geothermal plants in the U.S., located in California. Enel Green Power is expanding its geothermal portfolio across Europe and Latin America.
Energy developers play a crucial role in this sector. They explore geothermal resources and construct power plants. Their expertise in geothermal engineering ensures efficient energy use. As demand for clean energy rises, these companies will likely see increased investment.
Government Incentives
Government policies significantly impact the growth of geothermal energy projects. Many countries offer incentives to promote renewable energy development. The U.S. Department of Energy (DOE) has established the Geothermal Technologies Office to support research and innovation.
Tax credits and grants encourage investment in geothermal projects. For instance, the Investment Tax Credit (ITC) allows investors to deduct a percentage of their investment from federal taxes. This financial support makes geothermal projects more attractive.
Countries like Iceland and Kenya also provide favorable regulations for geothermal development. Their governments have implemented policies that streamline permitting processes. These measures help attract private investment into the geothermal lithium industry.
Future Outlook
The future of geothermal energy looks promising. As technology advances, efficiency in geothermal power generation improves. New drilling techniques reduce costs and increase access to deeper resources.
Public awareness of climate change drives demand for sustainable energy sources. Geothermal energy stands out as a stable and low-emission option. Its potential as a reliable power source continues to gain recognition.
Investors are keen on tapping into this new gold rush of renewable energy opportunities. With strong governmental support and innovative technologies, the geothermal sector is set for significant growth.
Benefits and Risks of Geothermal Investment
Financial Advantages
Investing in geothermal energy offers several financial benefits. First, it provides stable returns. Unlike fossil fuels, geothermal plants have low operating costs once established. They can generate electricity continuously, ensuring a steady income stream.
Geothermal projects often require high initial investments. However, they can lead to lower long-term costs compared to traditional energy sources. According to the U.S. Department of Energy, geothermal power plants can deliver energy at competitive prices. This makes them appealing for investors looking for reliable revenue.
Tax incentives also enhance the financial appeal. Governments often provide support for renewable energy projects. These incentives can significantly reduce upfront costs and improve profitability.
Geological Uncertainties
Geothermal investments come with risks, particularly geological uncertainties. Each site has unique characteristics that can affect energy production. Investors must conduct thorough geological assessments before committing funds.
Unexpected geological conditions can lead to project delays or increased expenses. For instance, drilling may not yield sufficient heat or water flow. This uncertainty can deter some investors from entering the market.
Investors should also consider the lifespan of geothermal resources. While many sites provide consistent energy for decades, some may experience depletion over time. Understanding these risks is essential for making informed investment decisions.
Market Stability
Geothermal energy investments offer more stability than fossil fuel markets. Fossil fuel prices fluctuate due to geopolitical tensions and supply chain issues. In contrast, geothermal energy relies on local resources that are less affected by global events.
Investors benefit from this stability during economic downturns. While fossil fuel prices may drop sharply, geothermal projects maintain their value. This resilience makes geothermal a safer option in volatile markets.
The long-term nature of geothermal projects further enhances investment security. Once operational, these facilities typically provide decades of reliable energy production. This contrasts sharply with the short-term nature of many fossil fuel investments.
Financial Returns from Geothermal Projects
ROI Calculations
Investing in geothermal energy can yield significant returns. The geothermal energy return on investment (ROI) typically ranges from 10% to 20%. This percentage depends on various factors, including location and market conditions.
The initial cost to develop a commercial geothermal well can be high. It often falls between $2 million to $5 million per well. However, once operational, these wells can produce energy for decades. The long-term benefits often outweigh the upfront expenses.
Funding Opportunities
Various funding opportunities exist for geothermal investors. Government grants and incentives are available in many countries. These programs aim to promote renewable energy sources. For instance, the U.S. Department of Energy offers financial assistance for geothermal projects.
Private investors also play a crucial role. Many venture capital firms focus on clean energy projects. They provide necessary funds in exchange for equity stakes. This arrangement helps reduce the financial burden on developers.
Successful Case Studies
Several successful geothermal projects demonstrate profitability. The Geysers in California is one notable example. It is the largest complex of geothermal power plants in the world. Established in the 1960s, it continues to generate electricity today.
Another successful project is Hellisheidi in Iceland. This facility produces both electricity and hot water for heating. The investment paid off quickly due to Iceland’s abundant geothermal resources.
These case studies highlight how careful planning and execution can lead to profitable geothermal energy ventures.
Financial Models
Different financial models are used to assess geothermal investments. One common model is the Power Purchase Agreement (PPA). It allows investors to sell energy at a fixed price over several years. This provides stable revenue streams.
Another model is the Feed-in Tariff (FiT). Governments set guaranteed prices for renewable energy production under this scheme. It assures investors of income stability.
Investors should also consider risk-sharing arrangements with partners. These partnerships can help distribute costs and increase project viability.
Sustainable Investment in Geothermal Projects
Environmental Benefits
Geothermal energy plays a significant role in achieving sustainability goals. It provides a clean alternative to fossil fuels. Unlike coal or natural gas, geothermal systems emit minimal greenhouse gases. This reduces overall carbon footprints. The U.S. Department of Energy notes that geothermal plants can lower emissions by up to 90% compared to traditional power sources.
The long-term environmental impacts of geothermal energy are favorable. Geothermal development has a smaller land footprint than solar or wind farms. Once established, geothermal power plants require less maintenance and have fewer ecological disturbances. Moreover, they utilize existing geothermal wells effectively. This efficiency minimizes the need for new land and resources.
Community Empowerment
Community-based geothermal projects promote local energy independence. These initiatives allow communities to harness their geothermal resources. They create jobs and stimulate local economies. For example, small-scale geothermal plants can provide reliable energy for rural areas.
Investing in community-focused geothermal projects enhances resilience against energy price fluctuations. Local control over energy production leads to more stable prices for consumers. These projects often prioritize sustainable practices, ensuring that the environment benefits as well.
Economic Viability
Geothermal energy projects offer economic advantages too. The initial investment may be high, but the long-term savings are substantial. Operating costs for geothermal plants remain low once they are established. They also provide consistent energy output, unlike some renewable sources that depend on weather conditions.
The International Renewable Energy Agency (IRENA) reports that geothermal operations can generate stable returns over time. This makes them attractive investments for both private investors and public entities.
Technological Innovation
Technological advancements improve the efficiency of geothermal exploration efforts. Enhanced geothermal systems (EGS) expand the potential for tapping into geothermal resources. These innovations increase the viability of geothermal power plants in various regions.
Investors should consider supporting research and development in this field. Funding new technologies can lead to breakthroughs that make geothermal projects even more effective and accessible.
Regulatory Support
Government policies also play a crucial role in promoting geothermal development. Several countries offer incentives for investing in renewable energy projects. These include tax credits and grants specifically for geothermal energy initiatives.
Such support encourages more investors to explore opportunities in this sector. As regulations evolve, the potential for growth within the geothermal network increases.
Innovations Driving Geothermal Growth
Drilling Efficiency
Advancements in geothermal technologies have made drilling more efficient. Traditional methods often faced challenges, such as high costs and long timelines. New techniques reduce these issues significantly. For example, researchers developed advanced drilling equipment that can penetrate deeper into the Earth’s crust. This equipment uses high-pressure water jets to break rock more effectively.
These innovations lower costs for geothermal projects. They also shorten the time needed to set up a geothermal site. By improving drilling efficiency, companies can extract geothermal heat faster and more economically.
Collaborative Efforts
Private companies and research institutions play crucial roles in advancing geothermal technology. Collaborations between these entities foster innovation. For instance, major energy firms partner with universities to develop new geothermal generation methods. These partnerships often lead to groundbreaking research.
One successful project involved a private company working with a national lab on enhanced geothermal systems (EGS). EGS allows for energy extraction in areas without hydrothermal resources. The collaboration led to improved techniques for creating reservoirs. This makes previously unusable sites viable for energy production.
Emerging Technologies
Emerging technologies enhance the viability of geothermal energy extraction. One promising area is the use of machine learning algorithms. These algorithms analyze geological data to identify optimal drilling locations. This technology helps avoid dry wells, which waste resources.
Another exciting development is the integration of geothermal heat with other renewable sources. Hybrid systems combine solar or wind energy with geothermal generation. This combination maximizes energy output and provides a stable supply.
e companies explore using hydrothermal resources in urban areas. Urban geothermal projects tap into existing infrastructure, making them easier to implement. These projects provide heating and cooling solutions for buildings while reducing reliance on traditional oil.
Future Outlook
The future of geothermal energy looks bright due to these innovations. As drilling becomes cheaper and more efficient, interest in geothermal projects will likely increase. Collaborations between private companies and researchers will continue to drive advancements.
Governments are also recognizing the potential of geothermal energy. Policies supporting clean energy initiatives encourage investment in this sector. With growing demand for sustainable energy sources, geothermal energy stands out as a reliable option.
Evaluating Environmental Benefits of Geothermal
Zero Emissions
Geothermal energy is a zero-emission source of power. This means it does not release greenhouse gases during operation. According to the U.S. Department of Energy, geothermal plants emit 97% less carbon dioxide than coal-fired plants. The shift to geothermal can significantly reduce our carbon footprint. This contributes directly to climate change mitigation efforts.
The energy produced from geothermal sources is sustainable and reliable. It helps combat climate change by reducing reliance on fossil fuels. Countries like Iceland and New Zealand have successfully integrated geothermal energy into their grids. Their experiences show how this energy source can lead to a cleaner environment.
Land Use
Geothermal plants require minimal land compared to other energy sources. For instance, solar farms and wind farms need large areas for installation. In contrast, geothermal facilities occupy only a fraction of that space. This results in less disruption to local ecosystems.
The ecological impact of geothermal projects is also lower. They do not involve large-scale deforestation or habitat destruction. A study from the National Renewable Energy Laboratory highlights that geothermal development can coexist with agriculture and wildlife conservation.
This efficient land use makes geothermal an attractive option for sustainable energy development. Communities can benefit from clean energy without sacrificing their natural surroundings.
Baseload Power
Geothermal energy provides stable baseload power. This means it can generate electricity consistently, regardless of weather conditions. Unlike solar or wind, which depend on sunlight and wind speed, geothermal operates continuously.
The reliability of geothermal power supports grid stability. It reduces the need for backup power sources, which often rely on fossil fuels. Research shows that countries utilizing geothermal energy experience fewer fluctuations in power supply.
Countries like the Philippines and Italy demonstrate successful integration of geothermal into their energy mix. They maintain stable electricity production while minimizing environmental impact.
Key Factors in Geothermal Investment
Location
Location plays a crucial role in geothermal energy projects. Access to high-quality geothermal resources is essential. Areas with volcanic activity or tectonic plate boundaries often have the best potential. For instance, the United States has significant geothermal resources in places like California and Nevada. These regions have proven reserves that can be tapped for energy production.
Geothermal plants need to be near these resources to reduce costs. Transportation of energy from remote areas can be expensive. Therefore, evaluating the geographical features and proximity to existing infrastructure is vital for project success.
Resource Availability
Resource availability directly impacts the feasibility of geothermal investments. Investors must assess the temperature and pressure of the geothermal reservoirs. High-temperature resources are more efficient for electricity generation. The ideal range typically falls between 150°C to 300°C.
Long-term sustainability of the resource is critical. Projects must consider how much energy can be extracted without depleting the reservoir. Studies and geological surveys help determine this potential. Accurate data ensures investors make informed decisions about their investments.
Regulatory Frameworks
Regulatory frameworks are another key factor in geothermal investment. Governments set rules that guide how projects are developed and operated. These regulations often include permitting processes, environmental assessments, and land use agreements.
Investors must navigate these frameworks carefully. They need to understand local laws and requirements. For example, obtaining permits can take time and may involve public consultations. Delays in this process can affect project timelines and budgets.
Understanding regulatory environments helps mitigate risks associated with geothermal investments. It also ensures compliance with environmental standards, which is increasingly important in today’s market.
Community Support
Community support significantly influences the success of geothermal projects. Engaging with local stakeholders early on builds trust and transparency. Communities often have concerns about environmental impacts or land use changes.
Successful projects frequently involve community input during planning stages. This engagement helps address concerns and fosters goodwill among residents. For example, educational programs about the benefits of geothermal energy can enhance public perception.
Communities that feel included in decision-making are more likely to support projects. Building strong relationships with local governments and organizations strengthens project viability.
Future of Geothermal Energy Investments
Investment Trends
Geothermal energy investments are set to increase significantly in the next decade. The global demand for clean energy drives this trend. Governments and private investors recognize the need for sustainable solutions. Countries like the United States, Iceland, and Indonesia lead in geothermal projects. These nations focus on expanding their geothermal exploration workforce.
The market dynamics point toward a forward-thinking approach. Investors prioritize renewable energy sources due to climate change concerns. Reports show that geothermal capacity could reach 200 gigawatts by 2030. This represents a substantial increase from current levels.
Role in Energy Transition
Geothermal energy can play a vital role in the global energy transition. It provides a stable and reliable source of power. Unlike solar and wind, geothermal is not dependent on weather conditions. This reliability makes it an attractive option for energy grids.
Many states are investing in geothermal projects as part of their clean energy targets. For example, California aims for 100% clean electricity by 2045. Geothermal can help achieve these ambitious goals while reducing carbon emissions.
Technological Advancements
Technological advancements enhance the scalability of geothermal projects. New drilling techniques reduce costs and time for exploration. Enhanced geothermal systems (EGS) allow extraction from previously untapped areas. These innovations expand the potential locations for geothermal plants.
Moreover, improved monitoring technologies increase efficiency in existing plants. Real-time data helps operators optimize performance and minimize downtime. As technology advances, more investors will likely enter the geothermal market.
Workforce Development
A growing geothermal exploration workforce is essential for future investments. Training programs and educational initiatives are crucial to prepare skilled workers. Many universities now offer degrees focused on renewable energy technologies.
States with active geothermal projects often create job opportunities in this sector. Skilled workers are needed for drilling, maintenance, and plant operations. This development adds economic benefits to local communities.
Closing Thoughts
Investing in geothermal energy is more than just a trend; it’s a smart move for your portfolio. You’ve learned about its potential, benefits, and risks. This sector is growing rapidly, driven by innovation and sustainability. The financial returns can be impressive, making it an attractive option for savvy investors like you.
As you consider your next investment, think about the long-term impact of geothermal projects. They not only promise profitability but also contribute to a healthier planet. Don’t miss out on this new gold rush. Dive into geothermal energy investments today and secure your place in a sustainable future. Your investment could pave the way for cleaner energy and better returns.
Frequently Asked Questions
What is geothermal energy?
Geothermal energy is heat derived from the Earth’s interior. It’s harnessed for electricity generation and direct heating applications, making it a renewable and sustainable energy source.
Why invest in geothermal energy projects?
Investing in geothermal energy offers long-term financial returns, sustainability benefits, and reduced reliance on fossil fuels. It’s a growing sector with increasing demand for clean energy solutions.
What are the risks associated with geothermal investments?
Risks include high upfront costs, geological uncertainties, and regulatory challenges. Investors should conduct thorough due diligence to mitigate these risks effectively.
How do financial returns from geothermal projects compare to other renewables?
Geothermal projects typically offer stable cash flows and lower operational costs compared to solar and wind. This can result in competitive returns over time, especially in favorable locations.
Are there innovations in the geothermal sector?
Yes, innovations like enhanced geothermal systems (EGS) and improved drilling technologies are driving growth. These advancements increase efficiency and expand potential geothermal resources.
How does geothermal energy benefit the environment?
Geothermal energy produces low greenhouse gas emissions and has a smaller land footprint compared to other energy sources. It contributes significantly to reducing climate change impacts.
What factors should I consider before investing in geothermal projects?
Consider location, technology maturity, regulatory environment, and financial stability of project developers. Understanding these factors helps ensure informed investment decisions.
 Send Buck a voice message!
Send Buck a voice message!




