Smart Textiles in Healthcare: Transforming Patient Monitoring and Care
Did you know that the global smart textiles market, including key insights on electronics, is expected to reach $5 billion by 2024? You can find free industry innovation reports on Google Scholar. Smart textiles and wearable sensors are revolutionizing health monitoring. They provide real-time data, making it easier to track vital signs and overall wellness. This technology is not just for athletes; it’s for everyone who cares about their health.
Investing in these innovative solutions can enhance personal healthcare management, as discussed in the overview article and feature papers on tao. With features like heart rate tracking and temperature monitoring, they empower users to take charge of their well-being. As the demand for personalized health solutions grows, smart textiles are becoming a game changer in the industry. Discover how these advancements can benefit you and transform your approach to health.
Key Takeaways
- Smart textiles and wearable sensors are revolutionizing health monitoring, making it essential for investors to explore this growing market.
- Understanding how smart textiles work can help you identify potential investment opportunities in innovative healthcare solutions.
- Wearable sensors provide real-time data, which can improve patient outcomes and reduce healthcare costs, making them a valuable addition to any health-focused portfolio.
- Be aware of the challenges facing smart textiles, such as durability and data privacy, to make informed investment decisions.
- Keep an eye on current innovations and trends in the market to stay ahead and capitalize on emerging technologies.
- Consider ethical implications and privacy concerns when investing in smart textiles and wearable sensors to ensure responsible investment practices.
Understanding Smart Textiles
Definition
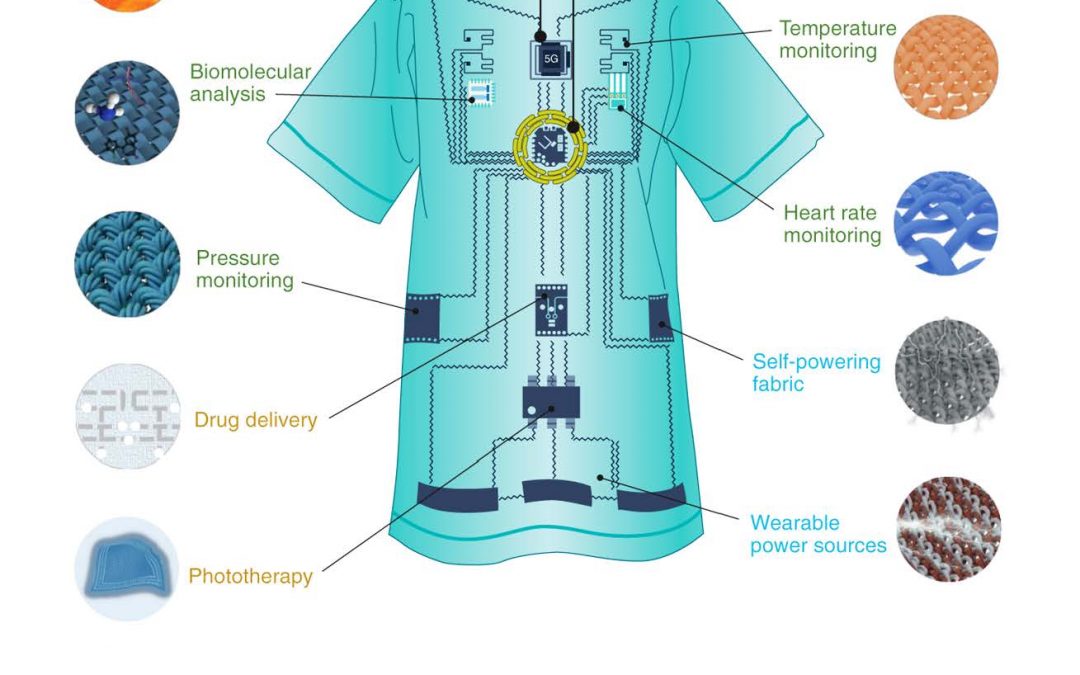
Smart textiles are fabrics that can sense and react to environmental changes. They differ from traditional fabrics because they incorporate technology within their fibers. This textile technology allows them to perform functions beyond mere clothing. For example, they can monitor health data or change color based on temperature.
Types of Smart Textiles
Various types of smart textiles exist today.
- Conductive Materials: These fabrics can conduct electricity. They often contain metallic fibers or conductive polymers. This feature enables them to connect with electronic devices.
- Sensing Materials: These textiles have embedded sensors that can detect physical conditions. They can measure heart rate, body temperature, or even muscle activity. This information is valuable in health monitoring.
- Responsive Materials: These fabrics respond to external stimuli. For instance, they might change color when exposed to sunlight or adjust their shape based on body movement. This adaptability makes them exciting for fashion and sports applications.
Applications in Healthcare
Smart textiles have significant potential in healthcare settings. Wearable sensors integrated into clothing can provide real-time health monitoring. Hospitals could use these textiles to track patient vitals without invasive methods.
For example, a shirt embedded with sensors could monitor a patient’s heart rate continuously. This data can alert medical staff if there are any irregularities. Such advancements improve patient care and reduce hospital visits.
Applications Beyond Healthcare
The applications of smart textiles extend beyond just healthcare.
In sports, athletes benefit from performance-monitoring garments. These clothes can track movements and provide feedback for improvement. Coaches and trainers can analyze this data to enhance training regimens.
Fashion designers are also exploring smart textiles. Clothing that changes color or pattern based on mood or environment is becoming popular. This innovation adds a new dimension to personal expression through fashion.
Market Growth
The market for smart textiles is growing rapidly. Research shows that the global smart textile market could reach $5 billion by 2024. The demand for wearable technology drives this growth. Consumers seek products that combine style with functionality.
Investors see potential in this sector as well. Companies developing smart textiles attract attention for their innovative solutions. The intersection of technology and fashion creates exciting opportunities for investment.
Role of Wearable Sensors in Health
Key Functions
Wearable sensors play a crucial part in health monitoring. They track vital signs like heart rate, temperature, and blood pressure. These sensors provide real-time feedback on the body’s status. This data helps users make informed health decisions.
For instance, athletes often use wearable sensors to monitor performance and recovery. They can adjust their training based on the information provided. Patients with chronic conditions benefit as well. Continuous monitoring allows for timely medical interventions.
Technology Behind Sensors
Biosensors are at the heart of wearable technology. They detect biological signals and convert them into readable data. Various types of biosensors exist, including electrochemical and optical sensors. Each type has unique applications in health monitoring.
Data transmission methods are also vital. Most wearable sensors connect via Bluetooth or Wi-Fi. This connection allows for seamless data transfer to smartphones or computers. Users can easily access their health metrics through apps. Cloud storage enhances accessibility, enabling healthcare providers to monitor patients remotely.
Importance of Real-Time Data
Real-time data collection is essential for proactive health management. It allows individuals to respond quickly to changes in their health status. For example, a sudden spike in heart rate can indicate distress. Immediate action can prevent serious complications.
Healthcare professionals can also use this data effectively. They can analyze trends over time and adjust treatment plans accordingly. This proactive approach improves patient outcomes significantly.
Wearable sensors also encourage healthier lifestyles. Many devices include features that promote physical activity and wellness. Users receive reminders to move or notifications about their health metrics. This engagement fosters awareness and responsibility for personal health.
Examples of Wearable Sensors
- Fitness Trackers: Devices like Fitbit monitor steps, heart rate, and sleep patterns.
- Smartwatches: Apple Watch tracks various health metrics and alerts users about irregularities.
- Health Patches: These adhesive devices monitor vital signs continuously without discomfort.
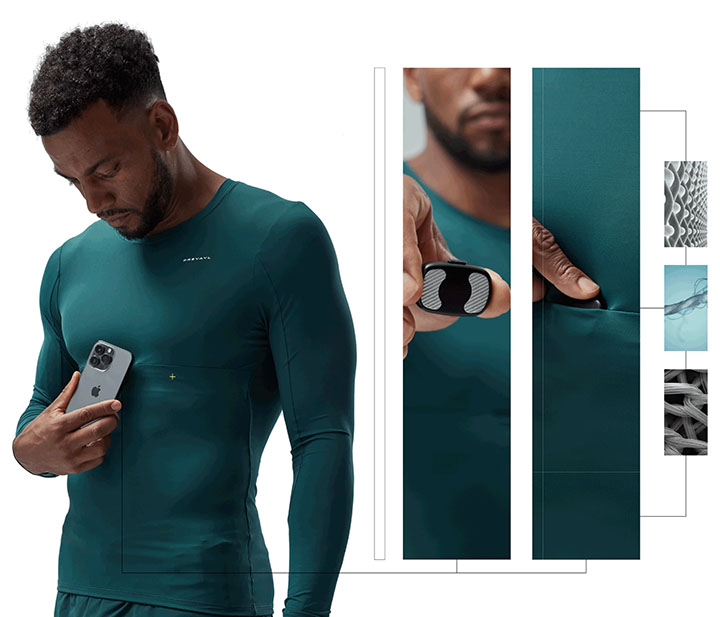
- Smart Clothing: Textiles embedded with sensors measure heart rates and muscle activity during workouts.
These examples illustrate how wearable sensors integrate into daily life, making health tracking more accessible.
Benefits of Smart Textiles in Healthcare
Enhanced Comfort
Smart textiles improve patient comfort significantly. These fabrics are designed to be lightweight and breathable. Patients can wear them without feeling restricted. This is crucial during health monitoring, as it allows for better mobility. For instance, a patient with chronic conditions can move freely while wearing these textiles. They do not interfere with daily activities.
Monitoring becomes less intrusive with smart textiles. Traditional sensors can be bulky and uncomfortable. In contrast, smart textiles integrate sensors into the fabric itself. This means patients can wear clothing that feels normal. They can go about their day without worrying about their health monitoring devices.
Continuous Monitoring
Continuous health monitoring is another key benefit of smart textiles. These textiles provide real-time data on vital signs. Heart rate, temperature, and other metrics are tracked seamlessly. This constant data collection can lead to early detection of health issues.
Fewer hospital visits result from this continuous monitoring. Patients can stay at home while still being monitored closely. This reduces the need for frequent check-ups. It also lowers healthcare costs for both patients and providers. According to a study by the American Journal of Medicine, remote monitoring can save up to 30% in healthcare costs.
Integration with Telemedicine
Smart textiles also enhance telemedicine capabilities. They allow healthcare providers to receive data remotely. This integration leads to improved patient outcomes. Doctors can monitor patients in real-time and adjust treatments as necessary.
Telemedicine combined with smart textiles supports timely interventions. For example, if a patient’s heart rate spikes, a doctor can take immediate action. This proactive approach can prevent complications and hospitalizations.
Communication improves between patients and healthcare providers. Patients feel more engaged in their care when they see real-time data about their health. They become active participants rather than passive recipients of care.
Summary
Smart textiles represent a significant advancement in healthcare technology. They enhance patient comfort and mobility during monitoring. Continuous health monitoring reduces hospital visits and healthcare costs. The integration of smart textiles with telemedicine improves patient outcomes significantly.
Challenges Facing Smart Textiles
Technical Issues
Developing durable and washable smart textiles presents significant technical challenges. Traditional textiles are not designed to incorporate sensors. Integrating electronics into fabric requires innovative materials that can withstand repeated washing.
Current technology often fails when exposed to water and heat. Sensors must be flexible yet robust enough for everyday wear. Researchers focus on creating materials that can endure these conditions without losing functionality.
Manufacturers also face issues with the longevity of the sensors used in smart textiles. Some sensors may degrade over time, affecting their accuracy. Ensuring that these fabrics remain reliable over an extended period is crucial for healthcare applications.
Regulatory Hurdles
Smart textiles must navigate complex regulatory landscapes before widespread adoption. Agencies like the FDA regulate medical devices, including wearable health monitors. This means smart textiles must meet strict safety and efficacy standards.
The approval process can be lengthy and costly. Companies may struggle with compliance due to the unique nature of textile-based devices. Each product requires thorough testing to ensure it meets all necessary regulations.
Furthermore, manufacturers need to demonstrate how these textiles benefit health monitoring. They must provide substantial evidence of reliability and effectiveness. This regulatory scrutiny can delay market entry and increase costs.
Market Acceptance
Consumer awareness plays a vital role in the acceptance of smart textiles. Many people are still unfamiliar with this technology and its potential benefits. Education about how these textiles work is essential for gaining trust.
Marketing strategies must focus on demonstrating the advantages of using smart textiles for health monitoring. Clear communication about the data they collect and how it impacts health is crucial.
Potential users may have concerns about privacy and data security as well. Addressing these issues openly can help build consumer confidence. Companies should provide transparent information on how data is collected and used.
Pricing can affect market acceptance. If smart textiles are too expensive, consumers may hesitate to invest in them. Finding a balance between affordability and quality will be essential for broader adoption.
Innovations Driving the Future
Recent Advancements
Recent developments in materials science have greatly improved smart textiles. Researchers focus on creating fabrics that can sense environmental changes. For example, conductive fibers now enable clothing to monitor heart rates and body temperature. These breakthroughs allow for more accurate health tracking.
Innovations in materials also include moisture-wicking textiles. These fabrics help keep users dry during physical activities. They can also be integrated with sensors to monitor sweat levels, which is crucial for athletes. This dual functionality makes them appealing for both casual and professional use.
Emerging Technologies
Emerging technologies significantly shape the future of smart textiles. Nanotechnology plays a key role in enhancing fabric capabilities. Tiny nanoparticles can be embedded into textiles to create features like stain resistance or UV protection. This application not only improves durability but also adds value to health monitoring by ensuring that sensors remain functional over time.
Artificial Intelligence (AI) is another game-changer. AI algorithms analyze data collected from wearable sensors. They can track patterns and provide insights about an individual’s health. For instance, AI can predict potential health issues based on historical data, allowing early intervention.
Future Trends
Future trends indicate that smart textiles will become more integrated into daily life. Wearable sensors will evolve beyond fitness tracking to include comprehensive health monitoring systems. These systems may detect conditions like diabetes or hypertension in real-time.
Developing features such as self-cleaning fabrics could also enhance usability. Imagine clothing that automatically cleans itself after exposure to sweat or dirt. This would make maintaining hygiene easier for users.
The implications of these advancements are vast. As smart textiles become more prevalent, they may reduce healthcare costs by enabling preventive care. Patients could manage chronic conditions at home, reducing the need for frequent hospital visits.
Researchers continue to explore possible research applications for smart textiles in various fields. From sports medicine to elder care, the potential is enormous. Recent articles highlight how these innovations can lead to personalized healthcare solutions tailored to individual needs.
Impact on Health Monitoring
The impact of these innovations is profound. Smart textiles will likely revolutionize how we approach health monitoring. With enhanced functionality, users can gain immediate access to vital information about their health status.

Integration with Digital Health Solutions
User Engagement
Smart textiles enhance health care capabilities by integrating with mobile health applications. These applications allow users to track their health metrics in real-time. For example, a smart shirt can monitor heart rate and send this data directly to a smartphone app. Users can receive alerts if their heart rate goes above or below normal levels. This direct engagement keeps individuals informed about their health.
Mobile applications also encourage users to set personal health goals. They can provide reminders to exercise, drink water, or take medication. The combination of smart textiles and mobile apps promotes active participation in health management. This user engagement leads to better outcomes.
Data Storage
Cloud computing plays a vital role in managing data from smart textiles. It allows for the storage of large amounts of information collected from various devices. For instance, data from multiple wearables can be uploaded to the cloud for analysis. This process ensures that users have access to their health insights anytime and anywhere.
Data analysis is crucial for identifying trends over time. Cloud-based systems can analyze changes in a user’s health metrics, providing valuable feedback. Health professionals can also access this data for more informed decision-making. They can monitor patients remotely and adjust treatment plans as needed.
Collaborative Ecosystems
Partnerships between tech companies and healthcare providers are essential for creating effective health ecosystems. Companies like Apple and Fitbit have collaborated with hospitals to integrate their devices into patient care. These partnerships ensure that smart textiles work seamlessly within existing healthcare frameworks.
By combining technology and healthcare expertise, these collaborations create comprehensive solutions. For example, a hospital may use smart textiles to monitor patients after surgery. The data collected can inform doctors about recovery progress without needing constant check-ups.
Such cohesive systems improve patient care and reduce costs. They enable healthcare providers to focus on prevention rather than just treatment. The integration of smart textiles into digital health solutions represents a significant shift in how healthcare is delivered.
Market Trends and Investment Opportunities
Current Growth
The smart textiles market is rapidly expanding. Recent reports show a projected growth rate of over 25% from 2023 to 2028. This surge is driven by increasing demand for health monitoring solutions. Consumers want products that can track their well-being in real time.
Innovations in technology play a crucial role in this growth. Wearable sensors embedded in fabrics provide accurate data about heart rates, body temperature, and more. These advancements make health management easier for users.
Key Players
Several key players dominate the smart textiles and wearable sensors market. Companies like Hexoskin and Fitbit lead the way with innovative products. Hexoskin offers shirts that monitor vital signs during workouts. Fitbit integrates fitness tracking with health metrics.
Startups are also emerging in this space. For example, Oura Ring focuses on sleep and recovery metrics. Their product tracks sleep quality through a simple ring design. Another startup, Myant, develops textiles that communicate with smartphones for health monitoring.
Investment Opportunities
Investors should consider opportunities in smart textiles and wearable sensors. The rising interest in health technology creates a favorable environment for investment. Stakeholders can explore various avenues, including startups and established companies.
Analytical reports indicate that the integration of smart textiles with digital health solutions will create new markets. Investors could benefit from backing companies that focus on telehealth and remote patient monitoring.
Investment in this sector offers potential high returns due to increasing consumer demand. Health-conscious individuals seek products that help them manage their wellness effectively.
Challenges Ahead
Despite the positive trends, challenges exist in the smart textiles market. High production costs can deter some companies from entering the field. Regulatory hurdles may slow down innovation.
Stakeholders must stay informed about these challenges. Understanding the market landscape helps investors make better decisions.
Ethical and Privacy Considerations
Data Collection
Collecting personal health data through smart textiles raises ethical questions. Users may not fully understand how their data is collected and used. Informed consent is crucial. Researchers must follow a strict research protocol to ensure participants know what they agree to. This includes clear information about the type of data collected and its purpose.
Many studies provide an overview of the data collection process. However, some lack transparency. Participants might feel uneasy if they do not receive adequate details about their involvement. The considerable literature findings indicate that ethical guidelines are often overlooked in practice.
User Consent
User consent plays a vital role in health monitoring technologies. Individuals should have the right to give or withdraw permission regarding their health data. This is especially important in wearable sensors, where continuous data collection occurs.
Privacy concerns arise when companies fail to secure user information. Data breaches can lead to unauthorized access to sensitive health information. Such incidents can damage trust between users and technology providers. Therefore, companies must implement strong security measures to protect data.
Transparent Policies
Transparent policies are essential for maintaining user trust. Regulations should clearly outline how user information will be stored and shared. Open access articles can help disseminate this information widely. They allow researchers and users to review publication details related to health monitoring technologies.
The preferred reporting items for systematic reviews can guide researchers in sharing their findings responsibly. This promotes accountability in the industry. Users need assurance that their data is handled ethically, following established guidelines.
Regulatory Framework
A robust regulatory framework is necessary for smart textiles and wearable sensors. Governments should establish laws protecting user privacy in health monitoring applications. These regulations must address publication limits on how much information can be shared without consent.
Companies should adhere to these regulations, ensuring compliance with ethical standards. Regular audits can help maintain accountability and transparency within the industry.
Final Remarks
Smart textiles and wearable sensors are changing the game in health monitoring. They offer real-time data, enhancing patient care and personal wellness. You can track vital signs, manage chronic conditions, and gain insights into your health like never before. While challenges exist, innovations are paving the way for a brighter future.
Investing in these technologies is not just smart; it’s essential. The market is ripe with opportunities, and your involvement can drive positive change. Embrace this shift towards smarter healthcare solutions. Stay informed, explore options, and consider how you can integrate these advancements into your life or business. Your health deserves it.
Frequently Asked Questions
What are smart textiles?
Smart textiles are fabrics embedded with technology that can sense and respond to environmental stimuli. They enhance functionality, enabling applications in health monitoring and other fields.
How do wearable sensors work?
Wearable sensors collect data from the body, such as heart rate or temperature. They transmit this information to devices for real-time health monitoring, providing valuable insights into personal health.
What are the benefits of smart textiles in healthcare?
Smart textiles improve patient care by enabling continuous monitoring, enhancing comfort, and facilitating early detection of health issues. They provide actionable data for both patients and healthcare providers.
What challenges do smart textiles face?
Challenges include high production costs, durability issues, and the need for regulatory approval. Integrating these technologies into existing healthcare systems can be complex.
What innovations are shaping the future of smart textiles?
Innovations include advanced materials, improved sensor technology, and enhanced connectivity features. These advancements drive efficiency and accuracy in health monitoring applications.
How do smart textiles integrate with digital health solutions?
Smart textiles can seamlessly connect with mobile apps and cloud-based platforms. This integration allows for comprehensive health tracking and data analysis, improving overall healthcare outcomes.
Are there privacy concerns with wearable sensors?
Yes, privacy concerns exist regarding data security and user consent. It’s crucial for manufacturers to implement robust encryption and transparent data policies to protect user information.
 Send Buck a voice message!
Send Buck a voice message!




